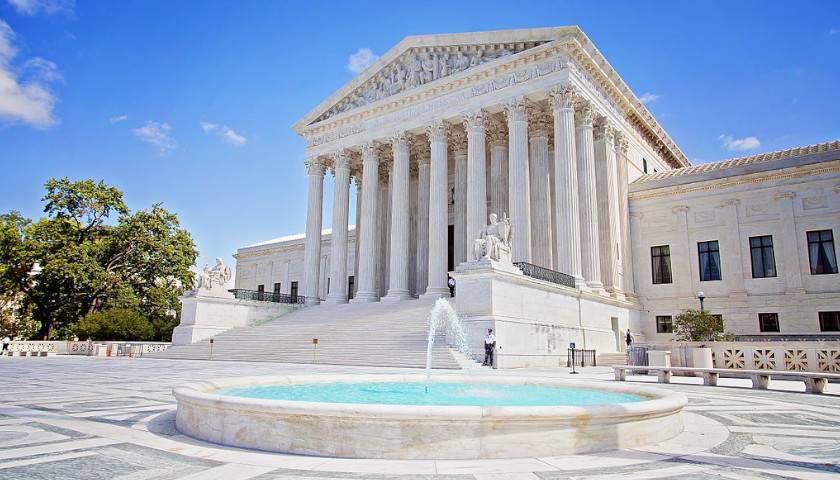
This summer the Supreme Court will rule on a case involving what a district court called perhaps “the most massive attack against free speech” ever inflicted on the American people. In Murthy v. Missouri, plaintiffs ranging from the attorneys general of Missouri and Louisiana to epidemiologists from Harvard and Stanford allege that the federal government violated the First Amendment by working with outside groups and social media platforms to surveil, flag, and quash dissenting speech – characterizing it as mis-, dis- and mal-information – on issues ranging from COVID-19 to election integrity.
The case has helped shine a light on a sprawling network of government agencies and connected NGOs that critics describe as a censorship industrial complex. That the U.S. government might aggressively clamp down on protected speech, and, certainly at the scale of millions of social media posts, may constitute a recent development. Reporting by RCI and other outlets – including Racket News’ new “Censorship Files” series, and continuing installments of the “Twitter Files” series to which it, Public, and others have contributed – and congressional probes continue to reveal the substantial breadth and depth of contemporary efforts to quell speech that authorities deem dangerous. But the roots of what some have dubbed the censorship industrial complex stretch back decades, born of an alliance between government, business, and academia that Democrat Sen. William Fulbright termed the “military-industrial-academic-complex” – building on President Eisenhower’s formulation – in a 1967 speech.
Read More